Maxar to study future systems for space-based comms for NASA
Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR) has been selected by NASA to study future systems that could revolutionize NASA’s space-based communications architecture through innovative technologies and commercial partnerships.

The future architecture would be used for scientific and human exploration missions in Earth orbit, at the Moon, and throughout the solar system beginning in the mid-2020s.
NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation Program currently offers space-based radio frequency communications services for all of the agency’s space communications activities via its Space Network. The Space Network consists of a constellation of geosynchronous satellites called TDRS and ground systems that operate as a relay system between satellites.
Leveraging current and planned commercial communication and navigation infrastructure, Maxar will study concepts to augment the Space Network with more advanced optical communications capabilities and enhanced radio frequency services.
Maxar will also study a framework that allows for a transition from government-owned and managed space services to commercially developed and operated services.
This future architecture could unlock the promise of human exploration, new and greater scientific discovery, and reduce development and operations costs for future missions through improved communication and navigation services.
Maxar has decades of experience in developing systems for space communications.
The company has built some of the world’s highest capacity spacecraft, including JUPITER™ 1/EchoStar XVII and JUPITER 2/EchoStar XIX — which power HughesNet® high-speed satellite internet service across the Americas.
Maxar is currently building JUPITER 3, which will provide more concentrated capacity over high-use areas than any other satellite.
Maxar has also contributed advanced concepts for the U.S. Air Force’s next-generation protected satellite communications architecture and has built more than 280 satellites, with 91 commercial communications satellites currently in service.
The operations of DigitalGlobe, SSL and Radiant Solutions were unified under the Maxar brand in February; MDA continues to operate as an independent business unit within the Maxar organization.
Megan Fitzgerald, Maxar’s Senior Vice President and General Manager of Space Solutions, said this award highlights Maxar’s ongoing commitment to the development of innovative space solutions that will open up a new realm of possibilities for human exploration. This future architecture will be designed to yield significant development and operations savings over government-owned systems and will also provide the benefit of frequent technology advancements.
www.maxar.com
www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/scan/index.html
The ThinSat 60 for STEM and research
Mission success can be claimed for the ThinSat 60 smallsat constellation, which was successfully launched by Virginia Commercial Space Flight Authority (VCSFA), Twiggs Space Lab, LLC (TSL) and NearSpace Launch Inc. (NSL) on April 17, 2019.
Co-founder of Twiggs Space Labs and Co-Inventor of the cubesat, Bob Twiggs, stated, “Our goal is to inspire future generations of engineers and scientists through innovation in the field of space.” Twiggs goes further to say, “To me, this (ThinSat launch) is the most exciting day of my career.”
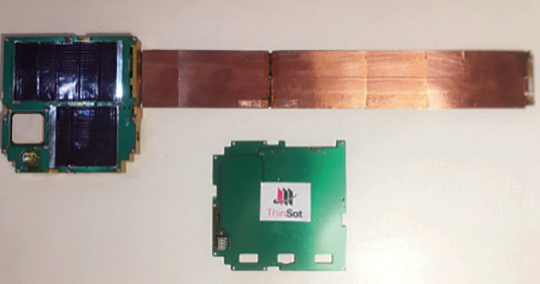
Figure 1. 60 ThinSat deployed in 3-string
and 6-string arrays The ThinSat is a new
pioneering model for satellites that are
scalable, simpler, and more affordable.
The focus is to broaden access to space
for educational and research participants.
VCSFA, TSL, NSL have worked with over
60 schools in training, testing and
delivering payloads for Extremely Low
Earth Orbit (ELEO). 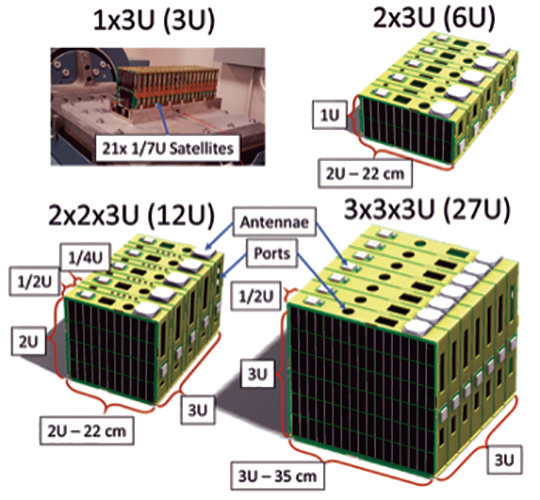
Figure 2: Scalable models of ThinSat from
3U to 27U in size. The ThinSat comes in an
array of sizes that comply with the CubeSat
launcher. The 11.2 cm by 11.7 cm by 2 cm
ThinSat version was the first model that
launched this April. The ThinSat team choose
to use NSL’s EyeStar radios and Alta Devices
(Alta) solar technology. The NSL’s EyeStar
radios allow for 24/7 connectivity via
Globalstar’s constellation. Alta’s solar cells
provide a unique modular, lightweight, flexible
and with high efficiency characteristics. 
Figure 3: Illustration of ThinSat deployed
in 3-string and 6-string arrays.
The ThinSat inventor and co-founder of NSL, Hank Voss, noted that ThinSats’ first constellation traveled in a region of the atmosphere that is important to climate and weather forecasts, but rarely studied because atmospheric drag makes it hard to keep satellites there.
Voss also expressed, that he is “thankful to Virginia Space and Twiggs Space Lab for funding and managing the project that had such a strong STEM outreach.”
More than 400 students were able to participate in the mission and see their experiment tested in orbit. All but two schools were able to receive data to engage in further analysis of there experiments.
The Deputy Director of NASA was able to attend and interact with the students. The affordable ThinSat program was accomplished though innovation, advanced manufacturing and great team work. The ThinSat was created by NearSpace Launch Inc.
The layout of the ThinSat is designed for advance manufacturing and scalability. Team work and partnership allowed for the ThinSat program to launch April 17, 2019.
www.nearspacelaunch.com
www.altadevices.com
twiggs-space-lab.myshopify.com
www.vaspace.org
Earth to Sky smallsat to launch with Delta Satellite Solutions
Earth to Sky, Inc. (ETS) has inked a definitive launch services agreement with Delta Satellite Solutions, Inc. (DSS) — the launch will occur in March 2021 to 550 km. SSO and will place 120 cubesats on-orbit.

Delta Satellite Solutions is a provider of affordable rides and payload and satellite integration services for academic institutions and was founded with the intention of connecting the STEM world to engage in real world experiences for space exploration.
Many universities and high schools provide the experience of designing, developing, and creating smallsats but few have the opportunity to put them in space.
Chris Barker, President of ETS, said the company is very excited to be working with DSS, supporting opportunities for educational institutions to fly cubesats. The company’s Sleek Eagle launch vehicle mated with the firm’s Cubesat Ring dispenser is capable of launching dozens of cubesats and other satellites on a single mission.
Evelyn Torres Bada, President of DSS, added that the educational market for cubesat missions is significantly underserved. Various STEM and government programs support development of satellites but not flying them and, as a result, there are hundreds of cubesats in colleges and universities around the world that are waiting for an opportunity to fly.
She added that the current high cost of flying cubesats, even as secondary payloads, has prohibited most from launching. The company’s price point is significantly under today’s costs and the firm plans to meet this large and growing need. DSS understands the tremendous educational value and motivation that being part of a satellite program operating in space can be for students at all levels. These un-launched satellites could become a significant boon for STEM related subjects when they are orbiting the Earth.
deltasatellites.com
Amazon Web Services reveals AWS Ground Station services
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS), an Amazon.com company (NASDAQ:AMZN), has announced the general availability of AWS Ground Station, a new service for customers to control satellites from AWS and download data from satellites into AWS Global Infrastructure Regions using a fully managed network of ground station antennas located around the world.
Once customers upload satellite commands and data through AWS Ground Station, they can quickly download large amounts of data over the high-speed AWS Ground Station network, immediately process it in an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance, store it in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), apply AWS analytics and machine learning services to gain insights, and use Amazon’s network to move the data to other regions and processing facilities.
Getting started with AWS Ground Station takes just a few clicks in the AWS Management Console to schedule antenna access time and launch an Amazon EC2 instance to communicate with the satellite. There are no up-front payments or long-term commitments, no ground infrastructure to build or manage and customers pay-by-the-minute for antenna access time used. To get started with AWS Ground Station, visit https://aws.amazon.com/ground-station
Satellites are being used by more and more businesses, universities and governments for a variety of applications, including weather forecasting, surface imaging, and communications. To accomplish this today, customers must build or lease ground antennas to communicate with the satellites. This is a significant undertaking and cost as customers often require antennas in multiple countries to download data when and where they need it without waiting for the satellite to pass over a desired location.
The antennas are just the start of the infrastructure requirements as customers need servers, storage, and networking in close proximity to the antenna to process, store, and transport the data from the satellite. Then customers must build business rules and workflows to organize, structure, and route the data to employees or customers before it can be used to deliver value. This requires significant capital investments and operational costs to build, manage, and securely maintain antennas, compute infrastructure, and business logic at each antenna location.
AWS Ground Station allows customers to more easily and cost-effectively control satellite operations, ingest satellite data, and integrate the data with applications and other cloud services running in AWS.
Using AWS Ground Station, customers can save as much as 80 percent of their ground station costs by paying for antenna access time on demand and they can rely on AWS Ground Station’s growing global footprint of ground stations to downlink data when and where they need it.
These ground stations are also located in close proximity to AWS Regions around the world, so customers can store, process, and analyze the data locally, rapidly gain insights, and then quickly take action.
The recency of data is particularly critical when it comes to tracking and acting upon fast-moving conditions on the ground. This timeliness depends on frequent communications between ground stations and satellites, which can only be achieved with a large, global footprint of antennas maintaining frequent contact with orbiting satellites.
For example, as fast-moving environmental, geopolitical, or news events unfold on the ground, AWS Ground Station customers can downlink current data to any of the AWS ground stations around the world. Customers can get timely data sooner, rapidly experiment with new applications, and deliver products to market faster without buying, leasing, or maintaining complex and expensive antennas and infrastructure. AWS Ground Station’s self-service graphical interface makes it easy to identify downlink opportunities, communications windows, and schedule antenna time. This enables customers to review confirmed times in the console and cancel or reschedule prior to the scheduled contact time.
Because AWS Ground Station antennas are located in close proximity to AWS Regions, customers have low-latency, local access to additional AWS services to process and store data. For example, they can use Amazon EC2 to control satellites and downlink data, store and share the data in Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS), Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS), or Amazon S3, use Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) for secure communications between Amazon EC2 instances and the AWS Ground Station antenna gateway, hunt for real-time business insights with Amazon Kinesis Data Streams and Amazon Elastic Map Reduce, apply machine learning algorithms and models with Amazon SageMaker, add image analysis with Amazon Rekognition, and improve data sets by combining satellite data with IoT sensor data from AWS IoT Greengrass. AWS Ground Station is available immediately in U.S. East (Ohio) and U.S. West (Oregon) and will expand to additional regions and locations in the coming year.
Shayn Hawthorne, GM, AWS Ground Station, said the goal of AWS Ground Station is to make space communications ubiquitous and to make ground stations simple and easy to use, so that more organizations can derive insights from satellite data to help improve life on earth and embark on deeper exploration and discovery in space.
Rohde & Schwarz has revealed their latest satellite uplink amplifier
For the first time in the U.S., Rohde & Schwarz presented their R&S® PKU100 Ku-band satellite uplink amplifier in an outdoor version at a recent satellite show.
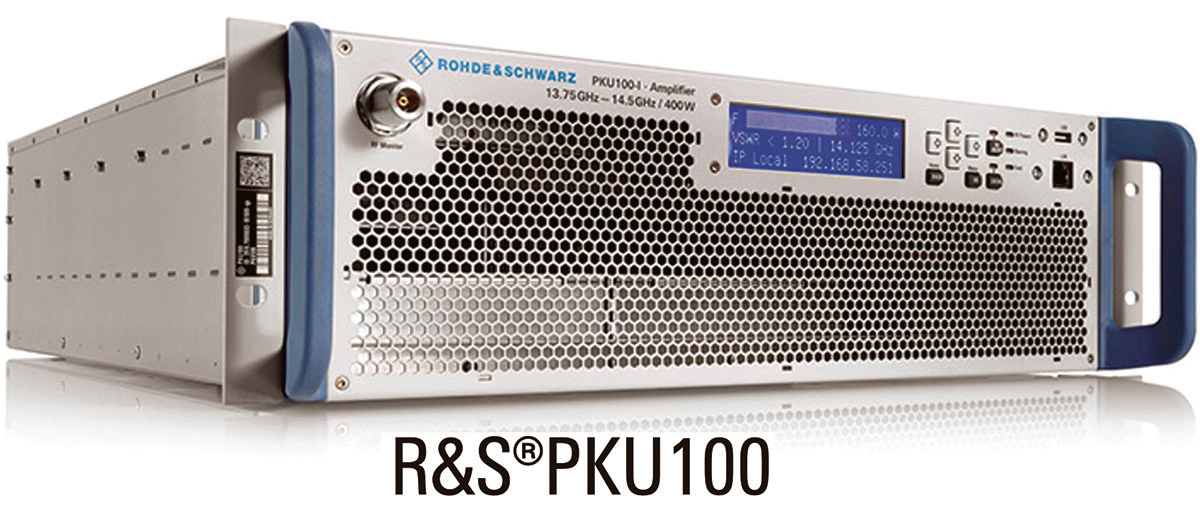

This uplink amplifier combines the best of two worlds in a single device: the unbeatable strengths of solid-state amplifiers and the compactness and low weight of tube amplifiers.
This weatherproof model is perfectly suited for outdoor applications and features all of the advantages of the indoor model.
The R&S PKU100 can be used in ground stations and satellite news gathering (SNG) vehicles.
Four models of the R&S PKU100 will be available, each in an indoor and an outdoor version.
The R&S PKU100 is obtainable for the 12.75 GHz to 13.25 GHz and 13.75 GHz to 14.5 GHz bands, with RF peak powers of 400 W and 750 W.
The solid-state power amplifier is just as light, compact and energy-efficient as conventional tube amplifiers and therefore clearly superior to comparable solid-state products.
The new outdoor models are particularly robust and weatherproof and comply with IP65 ingress protection specifications, plus they offer numerous features required for outdoor applications.
The R&S PKU100 can be mounted very close to the transmit antenna, saving RF power and minimizing capital and operating expenses.
Same as with the indoor model, the fans can be hot swapped in the event of a failure.
If fitted with an optional redundant power supply, the R&S PKU100 will continue operating should one of the power supplies fail.
The R&S PKU100 uses solid-state output stages throughout and offers a genuine alternative to conventional tube technology.
Should individual transistors fail, for example, the amplifier will continue operating at reduced power.
The R&S PKU100 is the only instrument on the market to offer adaptive linearization.
This improves signal quality, enabling network operators to transmit significantly more data over the same signal bandwidth. The amplifier offers excellent efficiency, reducing operating costs.
The R&S PKU100 can be fitted with a block upconverter (BUC), allowing low-frequency L-band signals to be processed and converted to the Ku-band.
The amplifier can be controlled remotely; it supports all common standards such as a web interface, SNMP, RS 232 and parallel I/O interfaces.
www.rohde-schwarz.compku100_233812.html
SOTM terminals now under development by Ovzon and GetSAT
Ovzon and GetSAT have signed an agreement to develop SATCOM-On-The-Move (SOTM) terminals
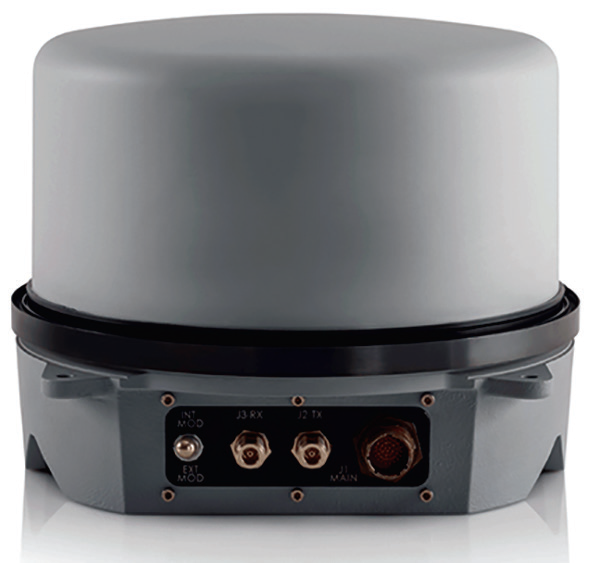

for the former’s global satellite service.
By combining SOTM terminals developed by GetSAT and Ovzon’s secure, end-to-end, mobile broadband satellite service, both companies strengthen their business opportunities for land, sea and air applications. This joint solution ensures SOTM broadband communications for defense, government, emergency response and broadcast customers worldwide.
The companies reached the strategic partnership after the successful testing and demonstration of GetSAT’s MicroSAT L/M (Land/Mobile) for Land and Maritime applications in Sweden and the United States. GetSAT’s terminals are based on the firm’s patented InterFLAT technology, which allows signals to be transmitted and received in the same panel, thus reducing the size, weight and energy consumption to provide advantages essential for the success of critical missions.
GetSAT’s MICRO SAT LM comprises a fully integrated (including BUC and Modem), fully ruggedized terminal that is optimized for all applications, and is ideal for demanding environments, such as in helicopters, boats, and vehicles.
GetSAT’s terminals are constructed in a light and compact installation. The L/M family of products are micronized, fully integrated, on-the-move, ruggedized solutions. All L/M terminals are easy to deploy and integrate, and can be outfitted with various antenna sizes in accordance with bandwidth requirements of ground, air and marine applications.
A unique all-in-one design including BUC and modem is optimized for harsh environments specs and its ultra-low power-consuming platform is compatible with Ka- and Ku-band applications.
Magnus René, the CEO of Ovzon, said that the company wants to address the need for SOTM services for land, maritime and airborne based applications with very small mobile broadband terminals for the firm’s global service. GetSAT provides a powerful solution with a very small footprint.
Kfir Benjamin, GetSAT CEO, reported that the firm is excited to announce this partnership with Ovzon. GetSAT’s low size, weight and power terminals are a perfect match with Ovzon’s robust and agile end-to-end service.
www.ovzon.com
www.getsat.com
The RISAT-2B satellite successfully launched by ISRO
India’s PSLV-C46 successfully launched the RISAT-2B satellite from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota.
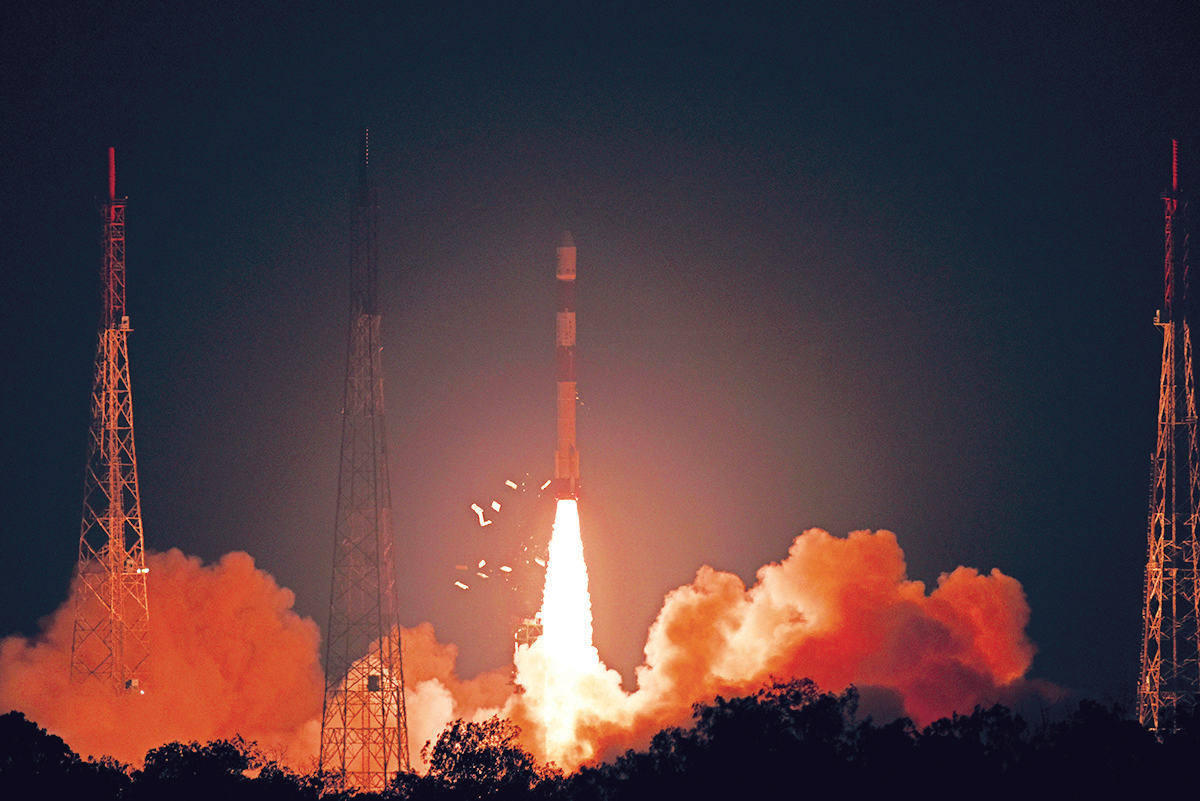

PSLV-C46 lifted-off at 05:30 Hrs (IST) on May 22, 2019, from the First Launch Pad of SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
PSLV-C46 was the 72nd launch vehicle mission from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
In this mission, the ‘Core-Alone’ configuration of PSLV was flown (without the use of solid strap-on motors).
About 15 minutes and 30 seconds after lift-off, RISAT-2B was injected into an orbit of 555 km at an inclination of 37 degree to the equator.
RISAT-2B with a lift-off mass of 615 kg, is a radar imaging Earth observation satellite.
The satellite is intended to provide services to Agriculture, Forestry and Disaster Management domains.
www.isro.gov.in/
HawkEye 360 and Windward combine forces for maritime domain awareness
HawkEye 360 Inc. and Windward have partnered to offer new global insights into maritime domain awareness through their combined capabilities — HawkEye 360 will contribute the firm’s RF dataset for use on Windward’s digital platform with select customers.

With HawkEye 360’s space-based RF geolocation services and Windward’s technology platform, a customer will be able to validate a vessel’s reported AIS location and continue tracking once the vessel has gone dark.
Windward will integrate HawkEye 360’s services into their platform to provide a seamless customer experience.
The partnership will demonstrate how RF analytics provides time critical insights for MDA that were previously impossible, offering significant value to Windward’s customer base.
The partnership between HawkEye 360 and Windward will help countries, law enforcement entities, financial institutions, and maritime insurers achieve domain awareness on a global scale.
Windward Co-Founder and CEO, Ami Daniel, said the company is committed to providing the firm’s clients with the biggest data and deepest insights to help them solve their maritime problems. That’s why the company is delighted to be working with HawkEye 360 and looks forward to exploring how RF geolocations and analysis can offer clients an even better service through enhanced risk modeling.
HawkEye 360 CEO John Serafini added that the Windward relationship aligns with the company’s strategy to partner with best in class organizations, servicing established markets that will significantly benefit from the firm’s first-of-its-kind global RF geolocation and analytic services.
www.he360.com/
wnwd.com/
M-ARGO mission assigned to GomSpace by European Space Agency
GomSpace’s subsidiary in Luxembourg and the European Space Agency (ESA) have signed a contract of 400,000 euros for the Phase A design of the Miniaturized Asteroid Remote Geophysical Observer (M-ARGO) mission.
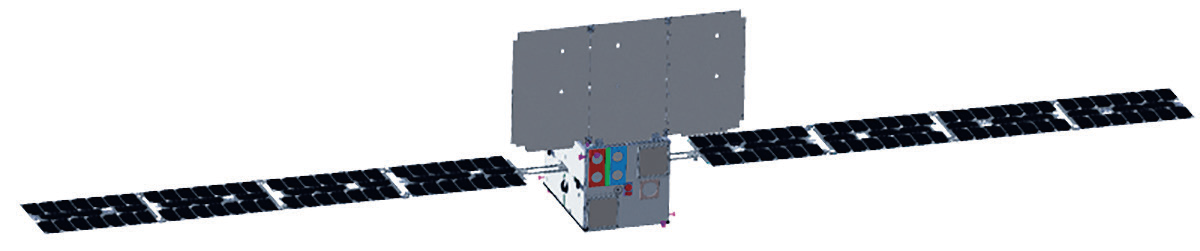
This preliminary concept illustration of the M-ARGO spacecraft
is courtesy of GomSpace.
Under the contract, GomSpace will be in charge of preliminary design of the mission, spacecraft and implementation planning.
A “12U” cubesat spacecraft configuration is envisioned for the mission, packing in beyond state-of-the-art advancements in miniaturized technologies including communication, instrumentation, electric propulsion and operational autonomy to be demonstrated in the deep space environment.
Expected launch of the mission is in 2023, subject to funding of the implementation phase, and it will be the first nanosatellite ever to rendezvous with an asteroid and perform close proximity operations over an extended period for identification of in-situ resources.
The NEO population now has more than 20,000 largely uncharted asteroids and the M-ARGO capability will be able to access the nearest 100 or more in terms of propellant needed to achieve a rendezvous.
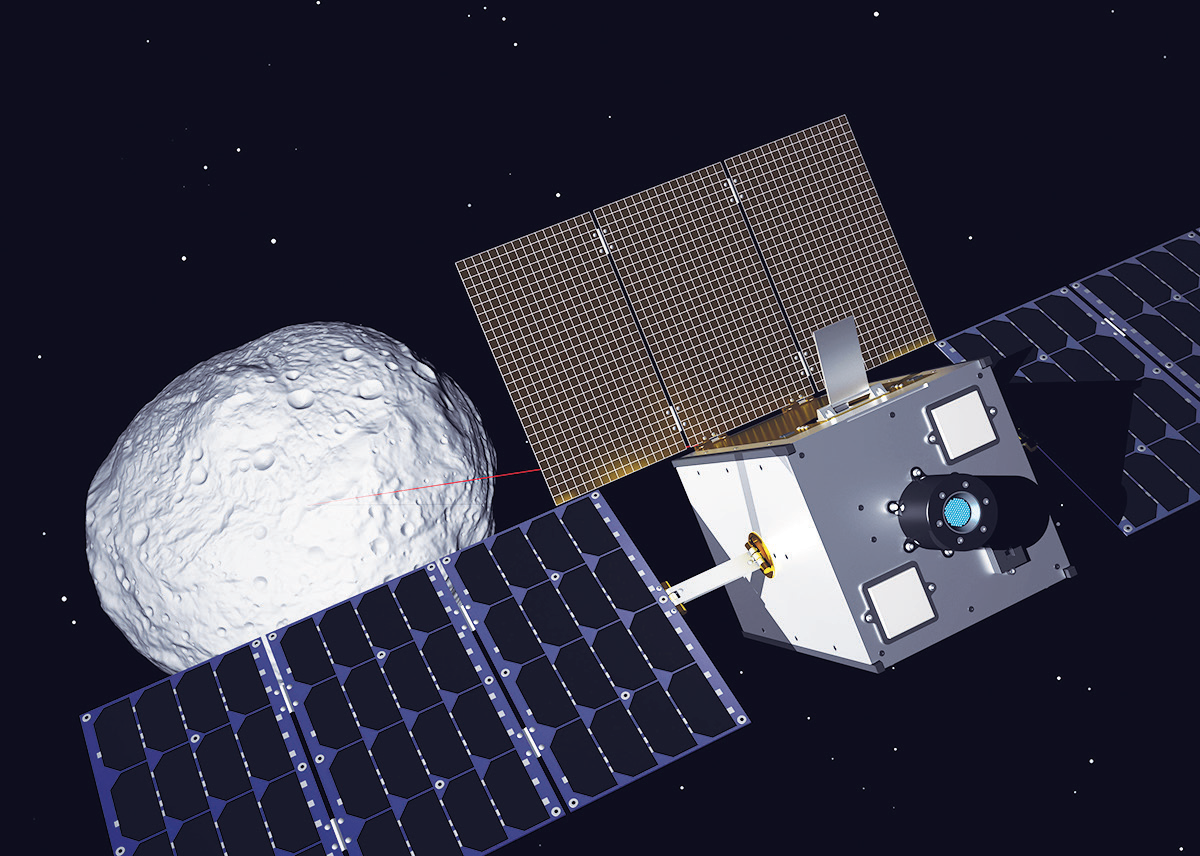

Artistic rendition of the M-ARGO spacecraft on
mission. Image is courtesy of ESA-Jacky Huart.
NEOs are interesting for scientific exploration as well as for the potential of future long-term exploitation of minerals and other useful materials mined from asteroids.
In addition, NEOs pose a threat for potential collisions with the Earth, requiring the need for further understanding of their physical properties for future planetary defense purposes.
Smallsat technology will allow future cost-efficient exploration of these objects in significant numbers. The work will be implemented in Luxembourg in line with GomSpace Group’s ambitions to benefit from the local space ecosystem. The work will be supported by the scientific-technological university, Politecnico di Milano in Italy, providing expert support on deep space mission analysis and navigation of low thrust trajectories associated with electric propulsion.
The contract is funded by the Luxembourg Space Agency through the Fly element of ESA’s General Support Technology Program (www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Engineering_Technology/Shaping_the_Future/About_the_General_Support_Technology_Programme_GSTP).
The mission implementation beyond the current phase A contract is open to further European cooperation as well as to consolidate the scientific requirements and propose the most suitable instruments for the mission.
Roger Walker, Head of ESA’s Cubesat Systems Unit, said the M-ARGO technology demonstration mission is intended as an enabler of a potential future operational capability for highly cost-effective in-situ resource exploration of the accessible Near-Earth Object (NEO) population using a fleet of deep space cubesats.
GomSpace CEO, Niels Buus, added that activities such as M-ARGO allow the company to develop the firm’s internal capabilities and technologies to new levels to the benefit of science and exploration as well as to build competitive advantage for the commercial markets. With these orders, GomSpace is satisfied to have built significant momentum for space exploration capabilities and positions the company well to serve ESA as well as other institutional customers on future, high-profile long duration missions.
www.gomspace.com
The Kleos Space Scouting Mission 1 now confirmed for a Rocket Lab Electron launch
Kleos Space S.A. (ASX: KSS, Frankfurt: KS1), (Kleos or Company) has revealed that the company’s Scouting Mission1 launch is confirmed for August 2019 on a Rocket Lab Electron launch vehicle.
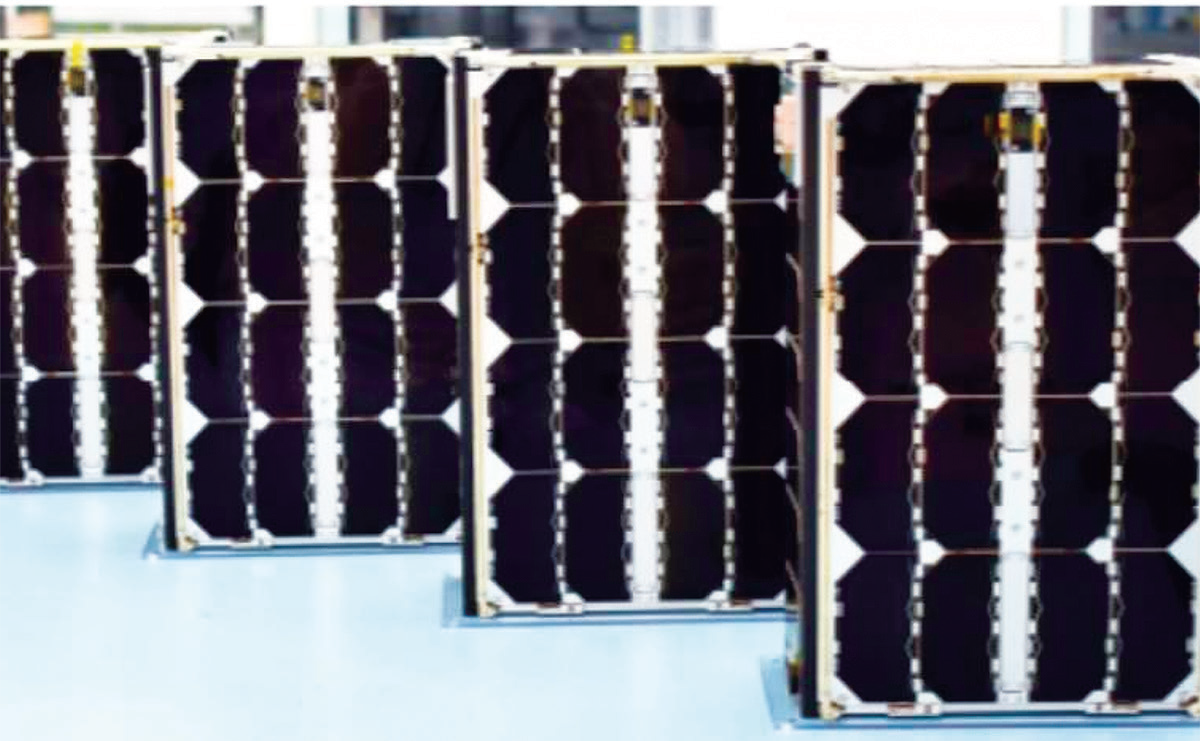
Assembled Kleos Scouting Mission smallsats.
Image is courtesy of the company.
All preparations by Kleos on the Kleos’ Scouting Mission satellites are on track for mission readiness and will be onsite, ready for flight preparation as soon as the Rocket Lab customer area is ready to accept the Kleos team for integration activities.
Satellite testing will conclude with a complete system test using KSAT (Kleos Scouting Mission ground station service provider) specialist ground station equipment, immediately prior to Flight Acceptance Review and dispatch to launch Site.
All four satellites have successfully completed all the necessary checks with the Rocket Lab’s in-house designed and built Maxwell dispenser which is used for deployment from the Electron kick stage to LEO.
Pre-flight testing of critical functions within the detection systems on the satellites used for the creation of the Kleos geolocation data, have performed significantly better than specification, this improvement will further increase accuracy and product value.
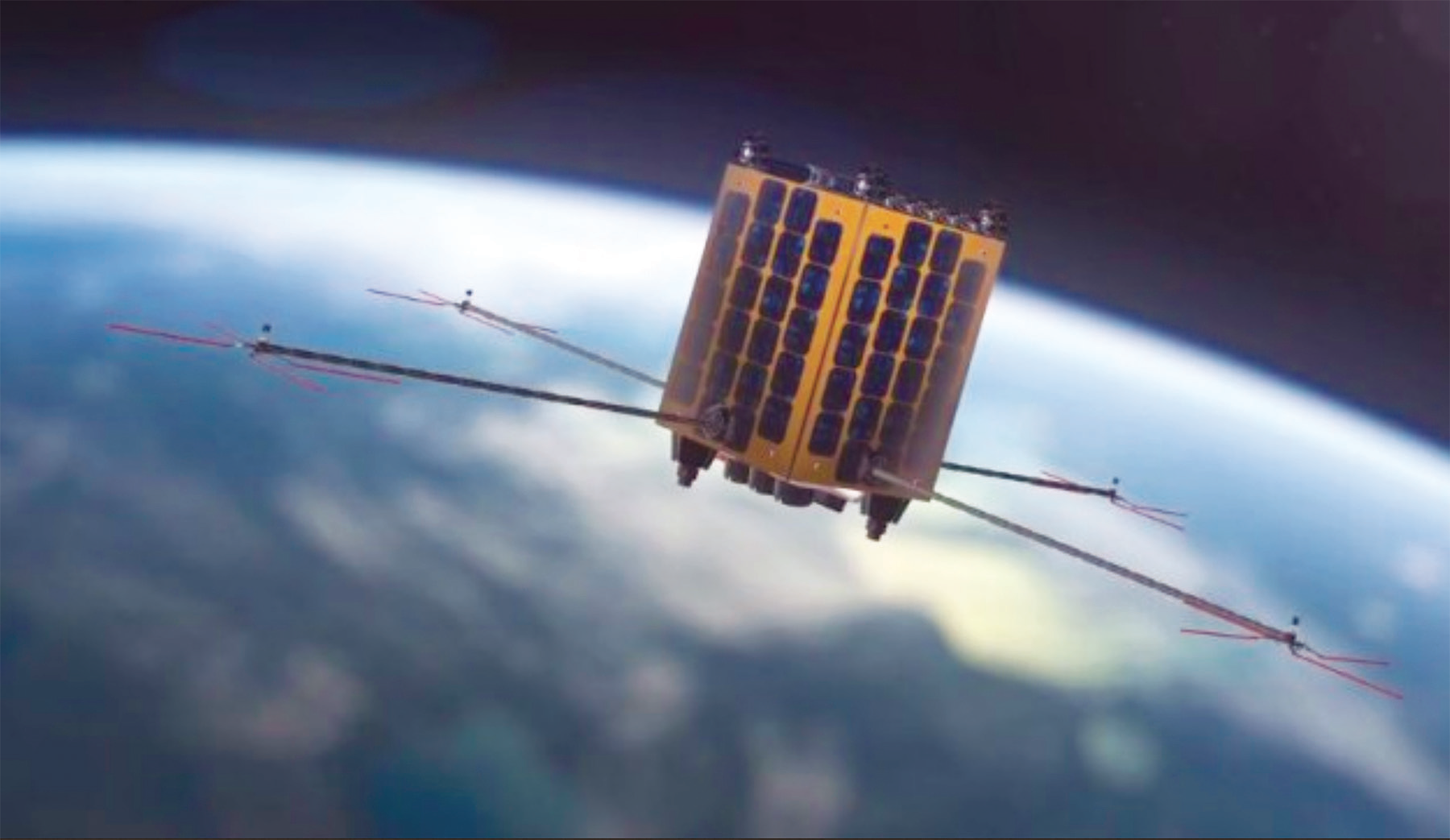

Artistic rendition of a Kleos Space smallsat on-orbit.
The Kleos’ Scouting Mission satellites are to be commissioned in a precise 500 km. SSO as part of a rideshare.
The first scouting mission is comprised of 4x smallsats built by GomSpace in Denmark, each the size of a shoebox.
The multi-satellite Scouting Mission system will form the foundation of a constellation that delivers a global picture of hidden maritime activity, enhancing the intelligence capability of government and commercial entities when AIS (Automatic Identification System) is defeated, imagery is unclear, or targets are out of patrol range.
Rocket Lab advised that the 14-day launch window will be publicly notified approximately 20 days prior to the target launch date.
Rocket Lab’s SVP of Global Launch Services, Lars Hoffman, said the company is excited to give the Kleos Scouting Mission satellites a first-class ride to orbit on Electron. The firm has worked closely with the Kleos team to design a tailored rideshare mission that lays the strong foundation for a future constellation.
kleos.space
www.rocketlabusa.com